General overview
What many companies and organizations are struggling with is the need for accurate and consistent information. For example, Telecom companies would like to have precise and synchronized product, customer, and service information to dynamically bundle and provide services.
In addition, companies should also take care of reporting, regulatory compliance, building service-oriented architecture (SOA), and other needs in the constantly changing landscape, which prompts a great interest in Master Data Management (MDM).
Fragmented, non-synchronized, and inconsistent master data in a company can produce supply chain inefficiencies, slow time-to-market, greater risk, and sales inefficiencies.
Effective information management can help companies eliminate errors, speed up their business activities, and improve critical processes such as service provisioning, product introductions, and customer services.
This article discusses what Master Data is and how it can be managed, enterprise data types, MDM problems, and the benefits of having an effective and reliable MDM solution.
What is Master Data?
Master Data is data that represents high-value business entities, concepts, and things of importance for the business overall, especially important for supporting transactional and analytical operations in the company. All larger enterprises store and manage master data as one of the key assets, for example, an ERP system could have master data about customers, items, and accounts.
Business objects around which the transactions are executed are represented by Master Data. This data also represents the key dimensions around which analytics are done. The goal of having an effective Master Data Management solution is to create a single version of the truth about these objects across the operational IT landscape.
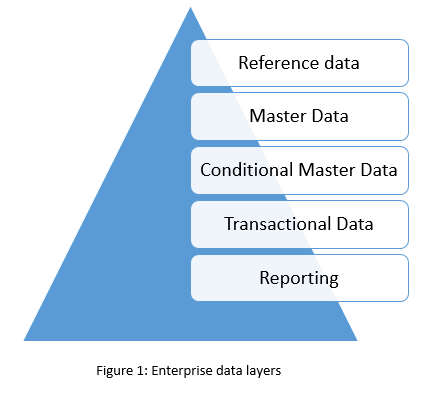
Enterprise Data Types
Reference Data is represented by reusable building blocks that combine to build Master Data: categories, colors, codes, types, etc.
Master Data is about the main business entities such as product, location, customer, vendor, etc.
Conditional Master Data is the intersection point for Master Data of different types, for example, effective dates of availability of Product by Location over Time. At this layer, a multiplication of master data can be observed.
Transactional data such as orders, sales, services, and deliveries produce an information explosion and the same product, location, vendor, and customer records are encountered hundreds, thousands, and even millions of times.
Reporting Data resides on the top of the other layers.
Any inconsistencies occurring upstream give rise to an equivalent explosion of inconsistencies downstream. The key lies in tackling the problem by creating a singular trusted representation of each piece of master or reference data, and a protective layer of governance in the form of appropriate rules and processes to keep it trusted and ensure that any new entities are similarly trusted.
Master Data problems
Most often, the Master Data of a company is stored and maintained in separate systems and applications with potential conflicts among the same entities, represented differently somewhere else. There is no single location to locate and work with an entity because of departmental solutions, functionally focused applications, geographic autonomy, etc.
This can lead to business intelligence inaccuracies and inconsistencies, “dirty information” and duplicates, multiple locations differently describing the same entity, data management conflicts, etc.
These data problems are breaking business processes, hindering Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems, corrupting analytics and significantly costing corporations.
What is Master Data Management?
Master Data Management (MDM) uses applications and technologies to combine, clean, and augment this business master data, to synchronize the data with all systems, business processes, and analytical tools. As a result, a company that implements a solid MDM solution can experience extensive improvements in operational efficiency, reporting, and fact-based decision-making. The Master Data Management (MDM) effort creates a System of Record (SOR) for business data, a golden master copy that is propagated to systems that have dependent data needs.
Master Data Management Benefits
Some of the main benefits of having a Master Data Management solution in an enterprise are:
- Guaranteed data consistency and reliable basis of information for all business operations
- Eliminated data redundancy in enterprise departments and disparate systems
- Improved data accuracy, detection of duplicates, and validation
- Unified process of master data editing and established flows for data update in all systems that work with master data
- Provided data flexibility regarding data storage, changes, availability, and usage
- Established effective data backup mechanisms that are crucial during disaster management and loss of data due to storage corruption and other failures
- Increased usability and business efficiency
- Supported intelligent and fast decision-enabling data reporting and analysis

